Creating a Filter, Edge Detection
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import cv2
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
# Read in the image
image = mpimg.imread('data/curved_lane.jpg')
plt.imshow(image)
# Convert to grayscale for filtering
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
plt.imshow(gray, cmap='gray')
TODO: Create a custom kernel
Below, you've been given one common type of edge detection filter: a Sobel operator.
The Sobel filter is very commonly used in edge detection and in finding patterns in intensity in an image. Applying a Sobel filter to an image is a way of taking (an approximation) of the derivative of the image in the x or y direction, separately. The operators look as follows.
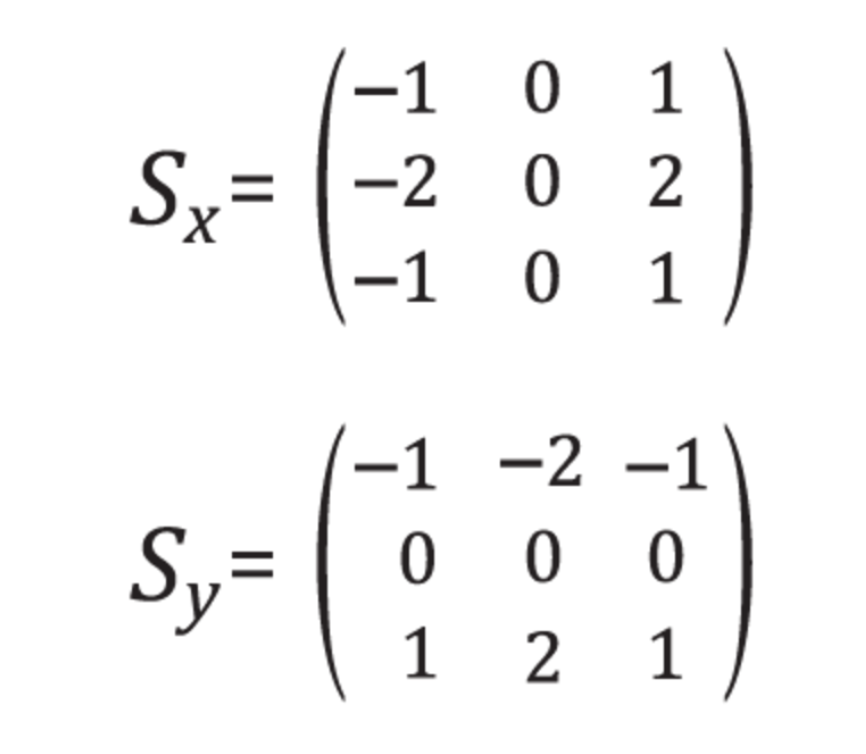
It's up to you to create a Sobel x operator and apply it to the given image.
For a challenge, see if you can put the image through a series of filters: first one that blurs the image (takes an average of pixels), and then one that detects the edges.
# Create a custom kernel
# 3x3 array for edge detection
sobel_y = np.array([[ -1, -2, -1],
[ 0, 0, 0],
[ 1, 2, 1]])
## TODO: Create and apply a Sobel x operator
# Filter the image using filter2D, which has inputs: (grayscale image, bit-depth, kernel)
filtered_image = cv2.filter2D(gray, -1, sobel_y)
plt.imshow(filtered_image, cmap='gray')